How to make a SIP voice call using C#?
 |
Download: | sip-make-voice-call.zip |
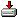
This example demonstrates how to make a SIP voice call with a softphone, written in c#.
First, you need to send the SIP REGISTER method to register the softphone with a
sip account to a pbx, than you have to send the SIP INVITE method to indicate
that a client is being invited to participate in a call session.
When all of these steps are done, the sip voice call setup is completed.
When the call is being accepted by the called party, the two parties are
able to communicate through their microphones and speakers.
To use this example, you need to have Ozeki VoIP SIP SDK installed,
and a reference to ozeki.dll should be added to your visual studio project.
What is voice call, how does it work with RTP?
During a voice call parties can communicate by sending and receiving voice stream data through the media devices, for example: microphone, speaker, which means that the voice data from a party's microphone arrives to the other party's speaker.
To implement the voice chat, when a party talks into the microphone, the stream of analog audio is being converted to a waveform, which represents the audio data with strings of numbers. Since the audio data is in digital format, it can be sent to the other party's speaker as RTP packages, through UDP connection. At the destination party the stream of numbers is being converted back into an analog voltage that can go to the speakers and be reproduced as sound (the voice of the user).
How to make SIP voice call using C#?
To perform a sip voice call in c# using Ozeki VoIP SIP SDK, you need to register
and ring the other party first, than ff the dialed party accepts the call,
the call's state changes to "Answered" and you are able to send and receive
audio data through the call. You need to solve C# microphone handling and
C# speaker handling, and you should connect the devices to the call through
media handlers to be able to send and receive voice data through the call.
Ozeki VoIP SIP SDK provides Media Handler for this purpose, for example the
Microphone, Speaker, PhoneCallAudioSender, PhoneCallAudioReceiver and MediaConnector classes.
Since the example is introducing this function by using softphone, you will probably use
system speaker and system microphone. Ozeki voip sip sdk also provides the opportunity to reach
pc default speaker and pc default microphone by calling only one method for each of them (see example).
SIP voice call example in C#
using System;
using Ozeki.Media;
using Ozeki.VoIP;
namespace SIP_Make_Voice_Call
{
class Program
{
static ISoftPhone softphone; // softphone object
static IPhoneLine phoneLine; // phoneline object
static IPhoneCall call;
static Microphone microphone;
static Speaker speaker;
static MediaConnector connector;
static PhoneCallAudioSender mediaSender;
static PhoneCallAudioReceiver mediaReceiver;
private static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a softphone object with RTP port range 5000-10000
softphone = SoftPhoneFactory.CreateSoftPhone(5000, 10000);
// SIP account registration data, (supplied by your VoIP service provider)
var registrationRequired = true;
var userName = "858";
var displayName = "858";
var authenticationId = "858";
var registerPassword = "858";
var domainHost = "192.168.115.100";
var domainPort = 5060;
var account = new SIPAccount(registrationRequired, displayName, userName, authenticationId, registerPassword, domainHost, domainPort);
// Send SIP regitration request
RegisterAccount(account);
microphone = Microphone.GetDefaultDevice();
speaker = Speaker.GetDefaultDevice();
mediaSender = new PhoneCallAudioSender();
mediaReceiver = new PhoneCallAudioReceiver();
connector = new MediaConnector();
// Prevents the termination of the application
Console.ReadLine();
}
static void RegisterAccount(SIPAccount account)
{
try
{
phoneLine = softphone.CreatePhoneLine(account);
phoneLine.RegistrationStateChanged += line_RegStateChanged;
softphone.RegisterPhoneLine(phoneLine);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine("Error during SIP registration: " + ex);
}
}
static void line_RegStateChanged(object sender, RegistrationStateChangedArgs e)
{
if (e.State == RegState.NotRegistered || e.State == RegState.Error)
Console.WriteLine("Registration failed!");
if (e.State == RegState.RegistrationSucceeded)
{
Console.WriteLine("Registration succeeded - Online!");
CreateCall();
}
}
private static void CreateCall()
{
var numberToDial = "853";
call = softphone.CreateCallObject(phoneLine, numberToDial);
call.CallStateChanged += call_CallStateChanged;
call.Start();
}
private static void SetupDevices()
{
connector.Connect(microphone, mediaSender);
connector.Connect(mediaReceiver, speaker);
mediaSender.AttachToCall(call);
mediaReceiver.AttachToCall(call);
microphone.Start();
speaker.Start();
}
static void call_CallStateChanged(object sender, CallStateChangedArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("Call state: {0}.", e.State);
if (e.State == CallState.Answered)
SetupDevices();
}
}
}
Stream of user voices sent as RTP packages
When the call has been successfully established, the 200 OK SIP message was
sent by the caller to the pbx to indicate the request was successful. At the same time,
users are able to send and receive stream of voice data
through their audio sender and audio receiver devices.
You can see the PDUs responsible for these below:
Step 1: softphone sends SIP OK message to the PBX to indicate the request was successful (UDP message, Softphone -> PBX)
SIP/2.0 200 OK Via: SIP/2.0/UDP 192.168.115.149:8061;branch=z9hG4bKac2d4f14-a833-4afc-b630- c132e0f9eca2;rport=8061; received=192.168.115.149 From: "1001"<sip:1001@192.168.115.149>;tag=njcgseol Call-ID: pceyekwevmyppmlqxujtflnrdfryvixbmmaallfdwojcljyskc CSeq: 2 INVITE To: <sip:9999@192.168.115.149>;tag=osrvmjgp User-Agent: Ozeki Phone System XE v5.2.1 Allow: INVITE, ACK, CANCEL, OPTIONS, BYE, REGISTER, SUBSCRIBE, NOTIFY, REFER, INFO, MESSAGE Content-Type: application/sdp Content-Length: 496 Contact: <sip:9999@192.168.115.149:5060> v=0 o=- 688704858 1556313105 IN IP4 192.168.115.149 s=Ozeki Call c=IN IP4 192.168.115.149 t=0 0 m=audio 8161 RTP/AVP 8 0 3 101 9 a=rtpmap:8 PCMA/8000 a=rtpmap:0 PCMU/8000 a=rtpmap:3 GSM/8000 a=rtpmap:101 telephone-event/8000 a=rtpmap:9 G722/8000 a=fmtp:9 bitrate=64000 a=sendrecv m=video 5466 RTP/AVP 34 102 99 a=rtpmap:34 H263/90000 a=fmtp:34 QCIF=1;CIF=1 a=rtpmap:102 H263-1998/90000 a=fmtp:102 QCIF=1;CIF=1 a=rtpmap:99 H264/90000 a=fmtp:99 packetization-mode=1 a=inactive
Step 2: the communication is working with RTP packages (a sample package)
[Stream setup by SDP (frame 28)] 10.. .... = Version: RFC 1889 Version (2) ..0. .... = Padding: False ...0 .... = Extension: False .... 0000 = Contributing source identifiers count: 0 1... .... = Marker: True Payload type: ITU-T G.711 PCMU (0) Sequence number: 7133 [Extended sequence number: 72669] Timestamp: 85000 Synchronization Source identifier: 0x712f7356 (1898935126) Payload: d55555545657545756565455575051575650515557515050...
Related Pages
More information
- How to build a softphone voip sip client
- Register to SIP PBX
- Voip softphone development
- How to encrypt voip sip calls with sip encryption
- How to encrypt voip sip calls with rtp encryption
- How to ring a sip extension csharp example for sip invite
- How to make a sip voice call using csharp
- Voip multiple phone lines
- How to send stream of voice data into call using csharp microphone
- How to receive voice from SIP voice call using csharp speaker
- How to make conference voice call using voip sip
- How to play an mp3 file into a voice call using csharp
- How to convert text to speech and play that into a call using csharp
- How to use Microsoft Speech Platform 11 for TTS and STT
- How to record voip sip voice call
- How to accept incoming call using csharp
- How to reject incoming call using csharp
- How to read Headset buttons using Bluetooth
- How to implement auto answer using csharp
- How to recognize incoming voice using speech to text conversion
- Voip forward call
- Voip blind transfer
- Voip attended transfer
- Voip do not disturb
- Voip call hold
- SIP Message Waiting Indication
- Voip DTMF signaling
- How to work with sip and sdp in voip sip calls
- How to work with rtp in voip sip calls
- How to make voip video calls in csharp
- Voip video codec
- Shows how to use SpeechToText Google API
- How to convert Text to Speech using C# and Google
- Azure Text-to-Speech
