Telephone systems
This page provides you an overview about telephone systems that are in use. After studying the following article you will be fully familiar with all the necessary terms and definitions related to key phone systems, traditional and IP PBXs and hybrid phone systems.
What is key phone system
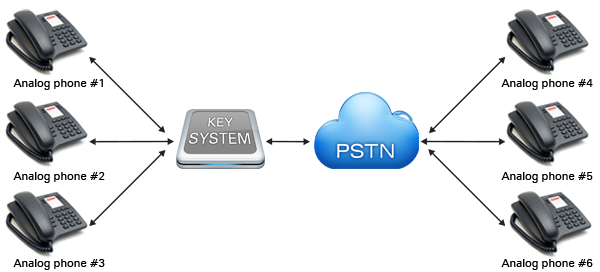
Small businesses widely deploy a key system or key telephone system that is a multiline telephone system. It has telephones with multiple buttons and lights indicating which of the lines is in use. To place a call a button needs to be pressed and a central office phone line of the telephone company will be directly selected. In key systems there is one unit that functions as a controller for a limited number of lines for a limited number of extensions. This unit can be an attendant phone or a separate box.
Key systems provide comfortable way of telephony by hold buttons, lights, intercoms, paging, speakerphones, privacy, timers, etc. Unlike PBX, Key systems allow the station user to see and control the calls directly, manually, using lighted line buttons. They are also expandable and offers individual line selection buttons for each of the connected lines.
Key systems can based on 3 main architectures:
- Electromechanical shared-control
- Electronic shared-control
- Independent keysets
On a typical key telephone system, each incoming central office line appears on a separate button on every key telephone set that is allowed to make or receive calls on that line. Usually, a visual indicator, such as a small incandescent lamp or light-emitting diode, allows the user to tell if the line is in use. The same lamp flashes at a certain rate when an incoming call is ringing on the line, and flashes at a different rate when a call is on hold. The number of lines that appear on every key telephone set varies with the capacity of buttons on each set. Such capacities vary from a low of 5 buttons to over 30 buttons, depending on the make and model of the key telephone system.
What is PBX
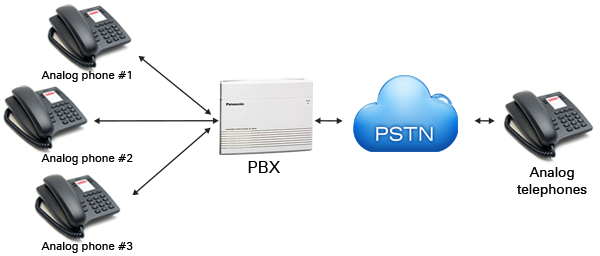
Private branch exchange (PBX) makes connections among internal telephones of an organization and also connects them to the public switched telephone network (PSTN) via trunk lines. Since equipment including telephones, fax machines, modems, and more are also incorporated, any end points of the system is referred to as "extension". It controls all the incoming and outgoing calls and connects outside callings with inside extensions and internal extensions with each other. There are fewer outside lines than extensions because all extensions will probably be not used at once.
The main advantages of PBX are the automated features, flexibility and easy setup. PBX can be customized, can have simple or sophisticated features, and individual lines may have different functions on them. Deriving from their architecture, PBXs also provide some access potential. Therefore, if access features are added to PBX, then any line connected to the system can use these features.
PBX is differentiated from Key systems in line selection. In case of key systems users need to select outgoing lines manually, while PBX selects outgoing lines automatically. PBX also employs a dial plan that is usually a single digit code. Users need to dial an escape code to be connected to an outside line. This code then is followed by an external number.
Due to the growing popularity of PBXs, they have been further developed. In this way services like call forwarding and extension dialing has been included. Later, because of the massive growth of data network and packet switching needs, VoIP PBX or IP PBX has been developed that allows packet switching over the Internet.
What is IP PBX (IP-PBX, IP/PBX or IPPBX)
IP PBX is a business telephone system developed to transfer voice or video over a data network. IP stands for Internet Protocol, PBX stands for Private Branch Exchange. IP PBX is a private system that switches calls between VoIP users on local lines and these users can also share some external phone lines. IP PBX systems are also able to interoperate with Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) and switches calls between a VoIP user and a traditional phone user or between two traditional phone users.
This functionality enables businesses to use their managed intranet to reduce long distance costs and benefit from a single network that is used for voice and data transfer providing greater mobility and cost effectiveness, while reduce redundancy. Since IP PBX deploys converged data and voice networks, Internet access, VoIP communications and traditional telephone communications are available using a single line to each of the users. This feature allows flexibility and long-term operation and maintenance costs can also be reduced.
The other benefit of IP PBXs is that it is quite cost effective and easy to add additional functionality to the system. In this way conferencing, XML-RPC control of live calls, Interactive voice response (IVR), TTS/ASR (text to speech/automatic speech recognition), Public switched telephone network (PSTN) interconnection ability supporting both analogue and digital circuits, Voice over IP protocols including SIP, etc can be included.
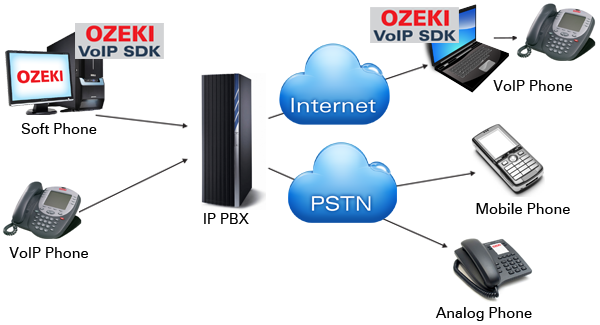
On Figure 3 you can see an IP PBX connection architecture. It demonstrates that soft phones and VoIP phones can connect to the IP PBX system to make calls. If you would like to call another VoIP phone user you can do so over the Internet. If you wish to call mobile phones or analog phones you can call them over PSTN.
VoIP phone system benefits
- 40-70% cost savings at installation
- 20-40% savings on monthly phone bills
- Seamlessly connects remote offices
- Easy to use, manage, and scale
What are hybrid keyphone systems
Hybrid keyphone systems support both analog and digital signaling. Modern key systems are usually digital (however, analog versions still occur), and some of them even support VoIP. In this way, today key systems also become small PBXs. The aspects that differentiate key systems from PBXs are amount, scope and complexity of the features and facilities offered.
What is PSTN
The Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) is the network of public circuit-switched telephone networks of the world. Primarily PSTN was a network of fixed-line analog systems but today it is an almost fully digital and it also include mobile and fixed telephones. It ensures worldwide availability with the combination of the interconnected networks and the single numbering plan.

